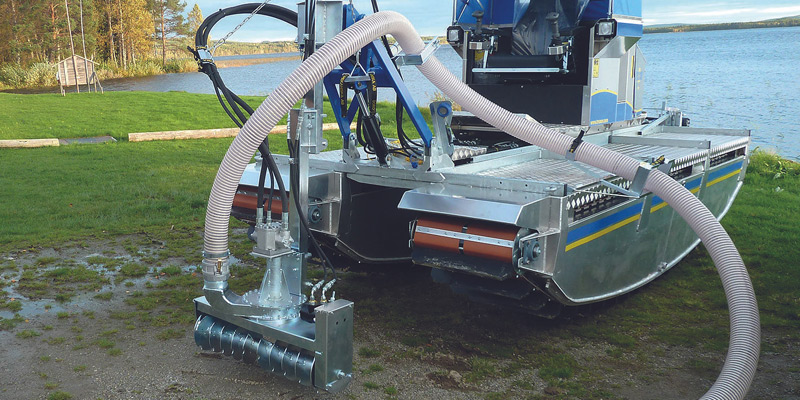
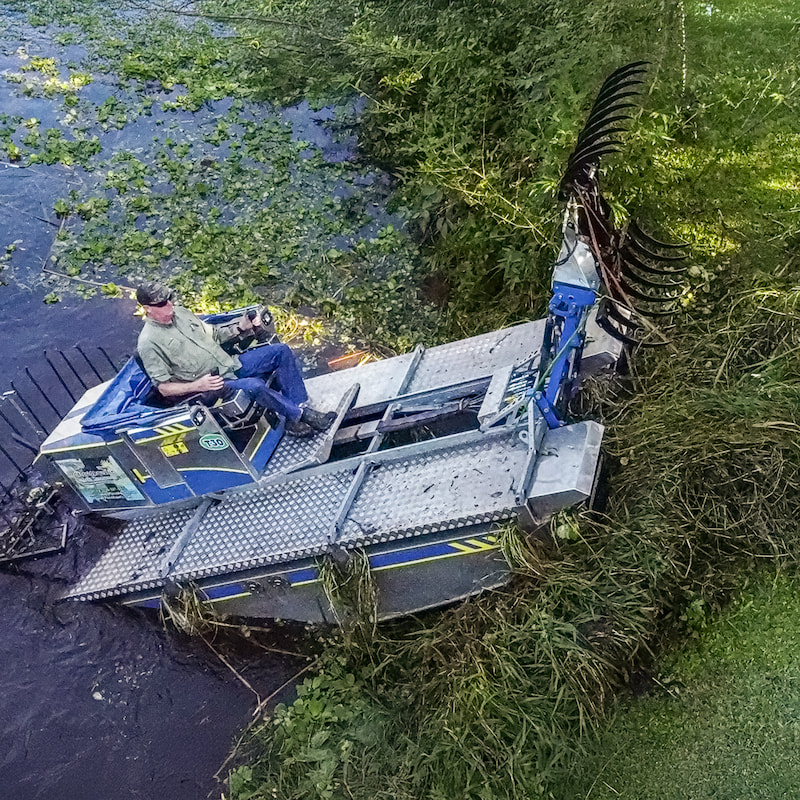
Pond dredging is most effective when the equipment matches the material being removed. In most ponds, the primary problem is the buildup of soft sediment, such as muck, silt, and organic sludge. That material requires steady intake, consistent flow, and minimal clogging. For Truxor operators, the attachments lineup includes a purpose-built solution for this exact work: the Doro Pump.
This article explains which attachment is best for pond dredging, why it is the best choice, how to configure it for deeper sediment zones, and which supporting attachments help complete the project efficiently.
Why the Doro Pump is the Best Primary Dredging Tool
The Doro Pump is the strongest primary option because it is designed to do the central dredging task well: remove bottom sediment as efficiently as possible.
Key reasons it is the best choice include:
Screw Feeder Intake for Steady Material Flow
The pump uses a screw feeder to break up and move sediment through the intake, which helps reduce blockages and supports uninterrupted dredging.
Suitable for Common Pond Environments
It is listed as working in both freshwater and saltwater environments, which supports use across a wide range of ponds and water bodies.
Designed for Sediment Control Applications
It is presented as ideal for sediment control in lakes, canals, and wetland basins, which aligns closely with typical pond dredging conditions and constraints.
Best Overall Dredging Setup for Most Ponds
For most pond dredging projects, the best setup is:
Doro Pump + Telescopic Extension
The Telescopic Extension (for Doro Pump) is the most practical upgrade when the pond has deeper pockets of sediment or when a greater reach reduces repositioning time. The extension is described as helping the pump reach deeper, up to nearly 8 feet, and it connects quickly with the Doro Pump system.
This configuration is especially effective for:
- Ponds with low spots and deeper basins where sediment accumulates
- Projects where you need additional reach without introducing larger equipment
- Sites where efficient positioning matters, such as retention ponds with limited access points
When the Best Choice is Not a Pump
Not every “dredging” scope is strictly pumping sediment. Some projects require excavation, trenching, or reshaping.
Choose the Doro Digger When Excavation and Shaping Are Required
If the project includes digging trenches, shaping shorelines, or handling tougher underwater excavation tasks, the Doro Digger is the more appropriate attachment. It is described as a high-tensile steel tool for challenging underwater work, including removing sediment, digging trenches, and shaping shorelines. It also includes channels and brackets that support attaching additional hydraulic tools for more complex work.
Common Doro Digger Use Cases Include:
- Cutting a trench or channel to restore flow paths
- Shoreline contouring and rehabilitation
- Removing compacted material where pumping alone is inefficient
Supporting Attachments That Improve Dredging Results
Pond dredging projects often involve more than sediment pumping. Debris, invasive vegetation, shoreline cleanup, and load-out efficiency can determine whether the project finishes smoothly. The following attachments are particularly useful before and after dredging passes.
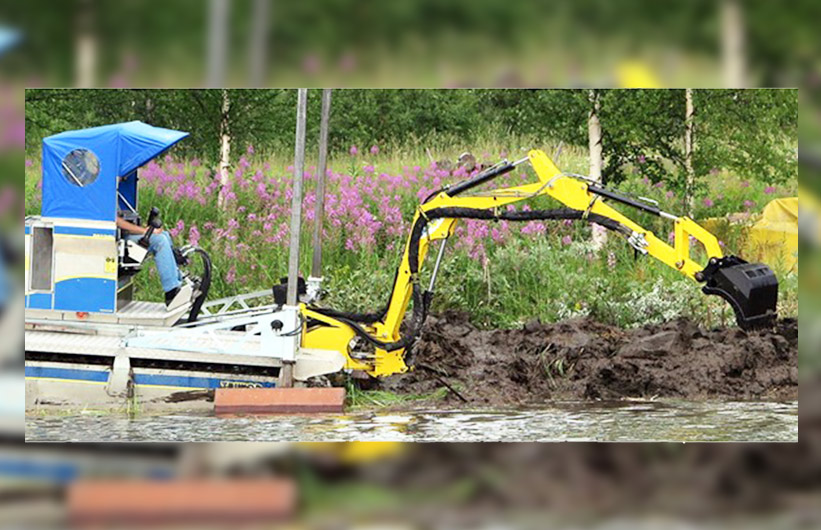

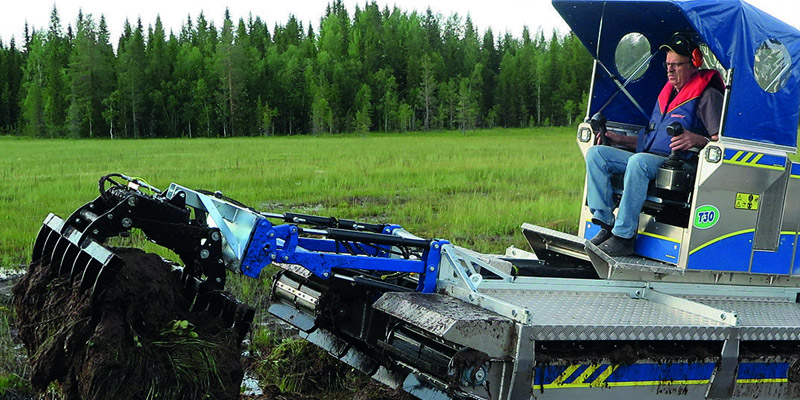
DoroGrip Bucket & Rake
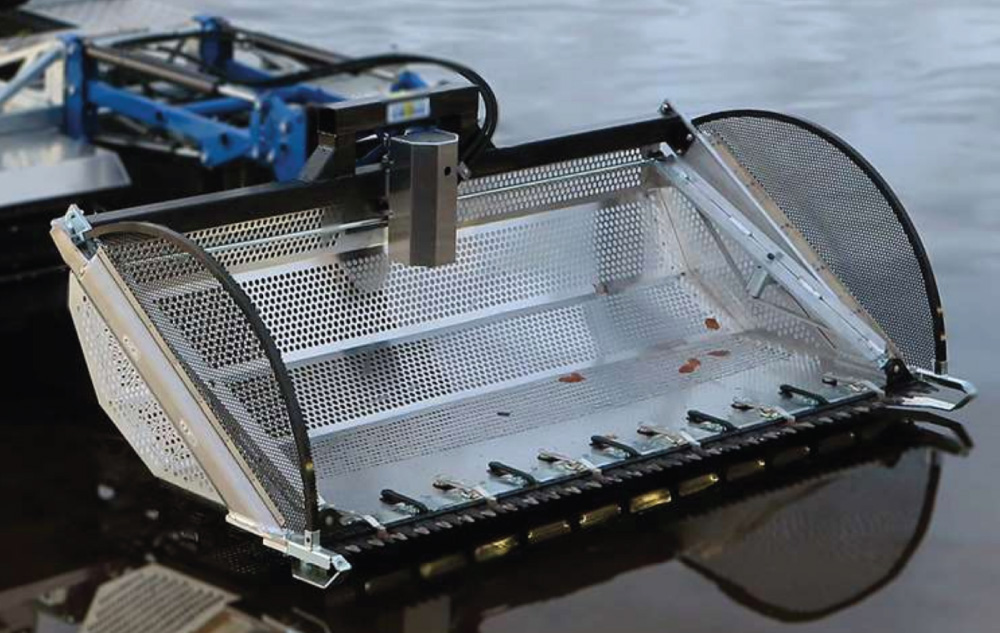
The DoroGrip Bucket & Rake is described as a heavy-duty tool for removing debris, sediment, and unwanted plants. It combines gripping and raking functions and is presented as useful for shoreline restoration, dredging support, and environmental recovery.
Where it helps most:
- Removing root systems, plastics, and bulky debris that can interfere with dredging flow
- Pre-cleaning problem areas before hydraulic dredging starts
- Pulling material into manageable zones for more efficient pumping and cleanup

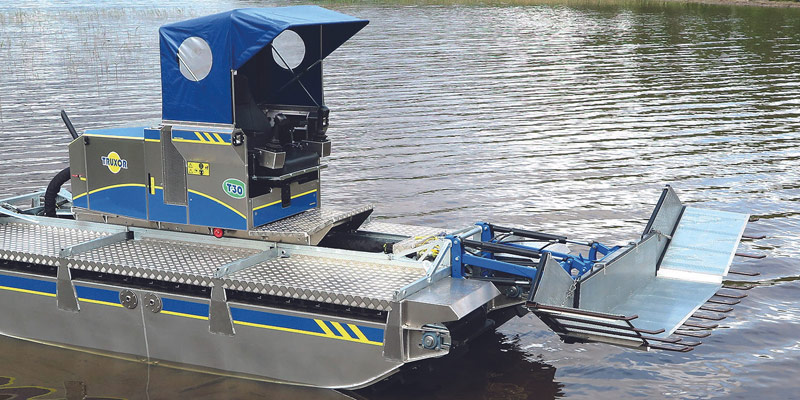
Reed Rake
The Reed Rake is described as a tool for collecting and moving aquatic plants after harvesting. It includes foldable sides for width adjustment, and optional strainer plates to catch smaller debris and algae.
Where it helps most:
- Clearing floating vegetation and loose material before dredging
- Post-dredge cleanup to improve site appearance and reduce floating waste

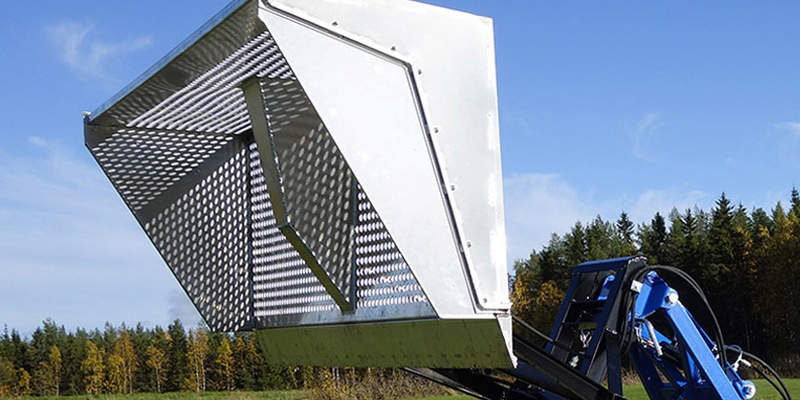
High Tip Rake
The High Tip Rake supports more efficient dumping into trailers, barges, or raised banks. Its perforated plate design is described as allowing water to drain while collecting debris like algae and grass, improving handling efficiency by reducing water weight.
Where it helps most:
- Load out and shoreline cleanup after dredging passes
- Reducing excessive water in collected material before transport

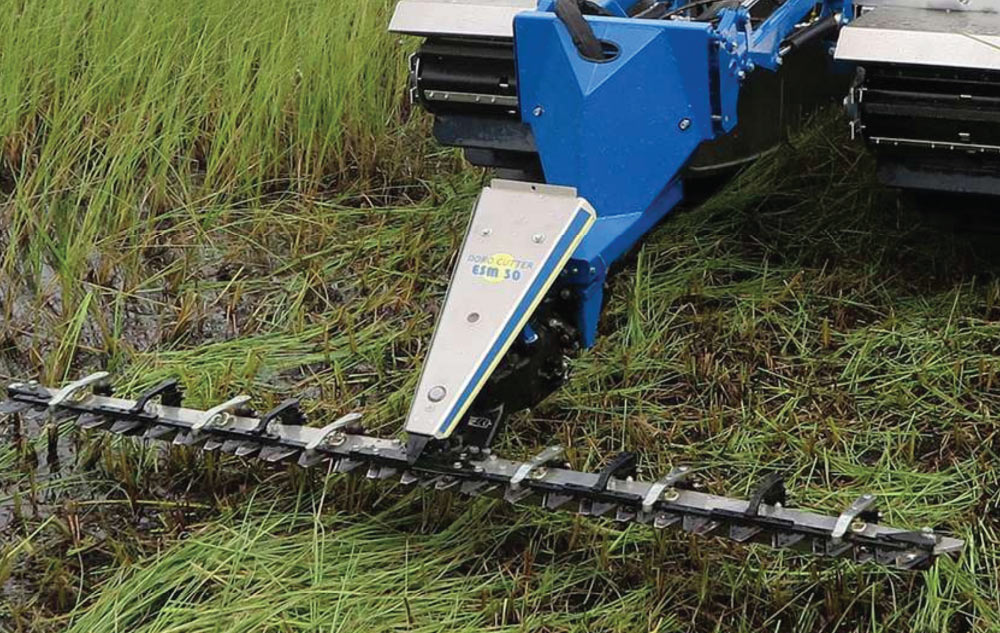
Vegetation Cutters (When Weeds Slow Down Dredging)
If a pond has dense vegetation, dredging productivity often improves when cutting and collection are performed first.
The attachments list includes cutters designed for different conditions:
- Doro Cutter ESM20, a front-mounted cutter with double-action knives and a stone release system, suited for shallow water precision work and narrow channels
- Doro Cutter ESM30, developed for challenging terrain such as wetlands, with dual-action knives capable of cutting plants and brush up to 0.78 inches thick
- Doro Cutter ESM50, an option that cuts and collects vegetation in a single operation using an integrated collection net


A Formal, Practical Workflow for Pond Dredging with Attachments
Below is a structured approach that reflects how pond dredging is commonly executed when vegetation, debris, and sediment are all present.
Step 1: Site Preparation and Surface Clearing
- Remove floating debris and vegetation mats using the Reed Rake when appropriate
- Use the DoroGrip Bucket & Rake to remove heavier debris and root systems that could obstruct the dredging intake flow
Step 2: Vegetation Cutting When Needed
- Select the cutter based on density and site constraints, for example, ESM20 for shallow, tight areas, or ESM50 when cut-and-collect efficiency is required
Step 3: Primary Dredging Passes with Doro Pump
- Conduct systematic passes over sediment zones, starting near inflows and low points where accumulation is typically greatest
- Maintain consistent positioning and intake depth to support steady flow and reduce turbidity spikes
- Leverage the pump’s screw feeder intake design to sustain continuous sediment feed when muck is organic or stringy
Step 4: Extend Reach for Deeper Sediment Zones
- Conduct systematic passes over sediment zones, starting near inflows and low points where accumulation is typically greatest
Step 5: Final Load Out and Shoreline Finish
- Use the High Tip Rake for efficient dumping into trailers or raised banks, while allowing water to drain through the perforated plate
- Perform a final cleanup pass with the Reed Rake to collect remaining floating material
For pond dredging, the best Truxor attachment is the Doro Pump, because it is designed specifically for sediment removal and includes a screw feeder intake that helps prevent clogging and maintain flow.
For most projects, the best overall configuration is Doro Pump + Telescopic Extension, since the extension increases reach to nearly 8 feet and improves access to deeper sediment zones.
When the scope requires excavation, trenching, or shoreline shaping, the Doro Digger is the appropriate attachment.
Truxor, The Best Equipment for Dredging
If you are planning a pond dredging project and want a solution that can dredge, cut, collect, and clean up using one platform, Truxor’s attachment system is designed for quick tool changes and multi-step pond work.
For pricing, machine selection, and a recommended Truxor attachment, contact Truxor Harvester USA at (239) 323-6444 to discuss your site conditions and goals.



